Innovation
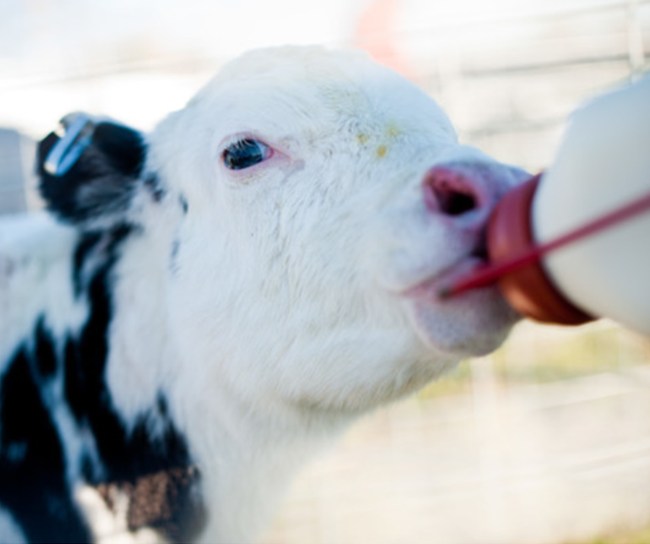
Humans, animals and the environment – our health is all connected
Why the One Health approach is important now more than ever
The health of humans, animals and the environment are all interconnected. When the health of one is at risk, the health of all may be at risk.
We see it in diseases transferred between animals or insects and humans (called zoonotic and vector-borne diseases) such as rabies, Lyme disease, West Nile virus, swine flu and Ebola, among others. We also see it in the growing threat from antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which occurs when bacteria mutate in ways that make the medicines (antimicrobials) used to treat infections ineffective, or when these medicines are used inappropriately to treat viral infections. Or, in diseases in food-producing animals, jeopardizing global food security.
Our increasing vulnerability to such new health challenges has led to a focus on “One Health” — an integrated approach to addressing human, animal and environmental health for the benefit of all.
What is One Health?
One Health is the collaborative approach across multiple disciplines — working locally, regionally, nationally and globally — to prevent, detect and respond to health issues at the interfaces between humans, animals and the environment.
It requires collaboration among doctors, veterinarians, nurses, public health practitioners, epidemiologists, agricultural workers, ecologists, wildlife experts, and industry as well as policymakers, communities and even pet owners.
“No one person, organization or sector can address these issues alone. Identifying and responding to growing health challenges requires teamwork,” says Holger Lehmann, DVM, Ph.D., VP, pharmaceuticals research and development, Merck Animal Health.
But what has led to these increasing population health threats?
Why are we more vulnerable to new health challenges?
Society has undergone major changes over the past century. While technology, increased mobility, industrialization, urbanization and globalization have advanced human, animal and environmental health in many ways, they’ve also made us more vulnerable to new health challenges.
For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, every year, millions of people and animals around the world are affected by zoonotic diseases. Scientists estimate that around 60% of emerging infectious diseases that are reported globally come from animals, both wild and domestic. Over 30 new human pathogens have been detected in the last 3 decades, 75% of which have originated in animals.
They can be spread in a number of ways, including direct or indirect contact, vector-borne, foodborne or waterborne. In fact, foodborne pathogens cause millions of cases of sporadic illness and chronic complications, as well as large and challenging outbreaks in many countries and between countries.
In addition, increased exposure to new viruses/bacteria combined with excessive and/or inappropriate use of medicines is causing a rise in AMR. Worldwide, an estimated 4.95 million people died with drug-resistant bacterial infections in 2019, and 1.27 million of these deaths were directly caused by antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Three main factors are fueling these population health threats, increasing the probability and speed of spreading diseases. They are:
Changes in climate and land use
Deforestation and other disruptions in environmental conditions can provide new opportunities for diseases to develop.
Exponential population growth and expansion into previously uninhabited areas
More people are living in close connection to their companion animals, and in some cases, closer to wild and domestic animals.
Increased international mobility
People, animals and animal products are moving more frequently, easily and widely than ever before.
Our commitment to One Health
With deep expertise in both human and animal health and a commitment to our shared environment, our company is well-positioned to be a leader in the One Health approach.
“We recognize the issues — such as zoonotic and infectious diseases and food safety and security — are interrelated,” says Ian Tarpey, Ph.D., VP, biological research and development, Merck Animal Health. “Our Animal Health and Human Health teams will continue to collaborate to discover and develop preventative solutions for existing and emerging diseases in animals and people.”
Our One Health approach focuses on many areas, including:
![icon]()
Disease prevention
We remain focused on discovering and developing vaccines and technologies to help prevent both human and animal diseases.
![icon]()
Surveillance and monitoring
We’re committed to advocating for and participating in scientifically based surveillance monitoring systems to better understand, track and predict health-related issues.
![icon]()
Respecting our environment
We support science-based, environmentally sound international and national programs to address the challenges to environmental health.
![icon]()
Innovation
Our human and animal health research laboratories collaborate in antimicrobial and vaccine research in many ways including sharing enabling technologies, expertise and evaluation of external opportunities. We’re also investing and developing predictive, monitoring and diagnostic technologies to help animal caretakers make data-driven evaluations of an animal’s health status and optimize their animals’ health and well-being.
![icon]()
Stewardship of essential medicines
We’re playing a leading role in addressing AMR by not only discovering and developing medicines and vaccines to treat and prevent infectious diseases in humans and animals but also supporting responsible use of these products.
![icon]()
Safe and sustainable food supply
We continue to work on developing vaccines and other tools to prevent animal disease to ensure a safe, nutritious, sustainable food supply, and we’ve implemented surveillance initiatives to enable more accurate risk profiling, early disease detection and individualized diagnosis/treatment decisions in livestock.
The science of healthier animals
We build strong partnerships in an effort to improve the health of animals around the world, and approach our work with a deep sense of responsibility — to our customers, consumers, animals, society and the planet.
Our work to promote optimal health continues
“One Health recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal and environmental health, acknowledging that the well-being of each is intricately linked. By embracing a collaborative approach, we can effectively address the complex challenges and promote optimal health for both humans and animals.”
– Dr. Jenelle Krishnamoorthy, VP, global public policy